Fats are one of the three main macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and proteins. Fat molecules consist of primarily carbon and hydrogen atoms and are therefore hydrophobic and are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in water. Examples include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides.
The terms lipid, oil, and fat are often confused. Lipid is the general term, though a lipid is not necessarily a triglyceride. Oil normally refers to a lipid with short or unsaturated fatty acid chains that is liquid at room temperature, while fat (in the strict sense) specifically refers to lipids that are solids at room temperature – however, fat (in the broad sense) may be used in food science as a synonym for lipid.
Fat is an important foodstuff for many forms of life, and fats serve both structural and metabolic functions. They are a necessary part of the diet of most heterotrophs (including humans) and are the most energy dense, thus the most efficient form of energy storage.
Some fatty acids that are set free by the digestion of fats are called essential because they cannot be synthesized in the body from simpler constituents. There are two essential fatty acids (EFAs) in human nutrition: alpha-linolenic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid) and linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid). Other lipids needed by the body can be synthesized from these and other fats. Fats and other lipids are broken down in the body by enzymes called lipases produced in the pancreas.
Fats and oils are categorized according to the number and bonding of the carbon atoms in the aliphatic chain. Fats that are saturated fats have no double bonds between the carbons in the chain. Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonded carbons in the chain. The nomenclature is based on the non-acid (non-carbonyl) end of the chain. This end is called the omega end or the n-end. Thus alpha-linolenic acid is called an omega-3 fatty acid because the 3rd carbon from that end is the first double bonded carbon in the chain counting from that end. Some oils and fats have multiple double bonds and are therefore called polyunsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats can be further divided into cis fats, which are the most common in nature, and trans fats, which are rare in nature. Unsaturated fats can be altered by reaction with hydrogen effected by a catalyst. This action, called hydrogenation, tends to break all the double bonds and makes a fully saturated fat. To make vegetable shortening, then, liquid cis-unsaturated fats such as vegetable oils are hydrogenated to produce saturated fats, which have more desirable physical properties e.g., they melt at a desirable temperature (30–40 °C), and store well, whereas polyunsaturated oils go rancid when they react with oxygen in the air. However, trans fats are generated during hydrogenation as contaminants created by an unwanted side reaction on the catalyst during partial hydrogenation.
Saturated fats can stack themselves in a closely packed arrangement, so they can solidify easily and are typically solid at room temperature. For example, animal fats tallow and lard are high in saturated fatty acid content and are solids. Olive and linseed oils on the other hand are unsaturated and liquid. Fats serve both as energy sources for the body, and as stores for energy in excess of what the body needs immediately. Each gram of fat when burned or metabolized releases about 9 food calories (37 kJ = 8.8 kcal). Fats are broken down in the healthy body to release their constituents, glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol itself can be converted to glucose by the liver and so become a source of energy.=
Examples of fatty acids.trans Unsaturated (Example shown: Elaidic acid)cis Unsaturated (Example shown: Oleic acid)Saturated (Example shown: Stearic acid)![]()
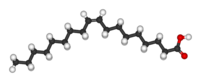
![]() Elaidic acid is the principal trans unsaturated fatty acid often found in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.Oleic acid is a cis unsaturated fatty acid making up 55–80% of olive oil.Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid found in animal fats and is the intended product in full hydrogenation. Stearic acid is neither cis nor trans because it has no carbon-carbon double bonds.
Elaidic acid is the principal trans unsaturated fatty acid often found in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.Oleic acid is a cis unsaturated fatty acid making up 55–80% of olive oil.Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid found in animal fats and is the intended product in full hydrogenation. Stearic acid is neither cis nor trans because it has no carbon-carbon double bonds.
